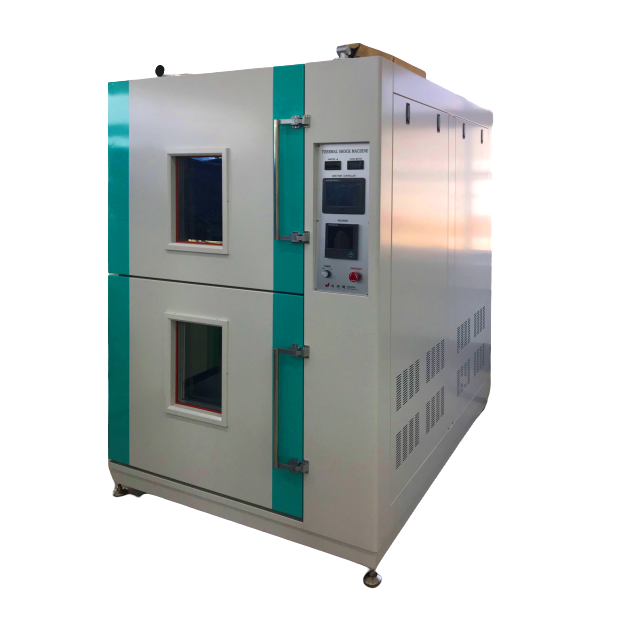

Guide to choose Thermal shock test chamber
09:13 - 08/07/2020
The thermal shock test is the test of the specimen’s strength to a sudden change in temperature (from the hot to cold temperature), also the high and low temperature test with high safety and reliability checks.
What is HALT and HASS testing?
How to choose Temperature & Humidity test chamber?

This type of testing helps check the reliability of the product in a short time, confirm the durability of products before it is released to the market.
In particular, the test is carried out when the specimen is subjected to repeated thermal cycles producing low or moderate frequency mechanical stress. DUT (Device under test) will tend to deform a non-linear way due to the different expansion coefficients of the materials. In fact, the specimen will be subjected to expansion and contraction in volume, includes strong mechanical stress, sometimes lead to breakage if the thermal shock rate of the product is greater than the maximum resistance of the material.
Choose the suitable thermal shock test chamber
It is essential that the thermal shock test chamber is selected and used to ensure the performance of the products under test. If you do not choose the most suitable equipment, the test performed cannot properly simulate "thermal shock".
For example, if the air circulation in the chamber is insufficient for heat absorption due to the test piece, the following may occur:
CASE 1:
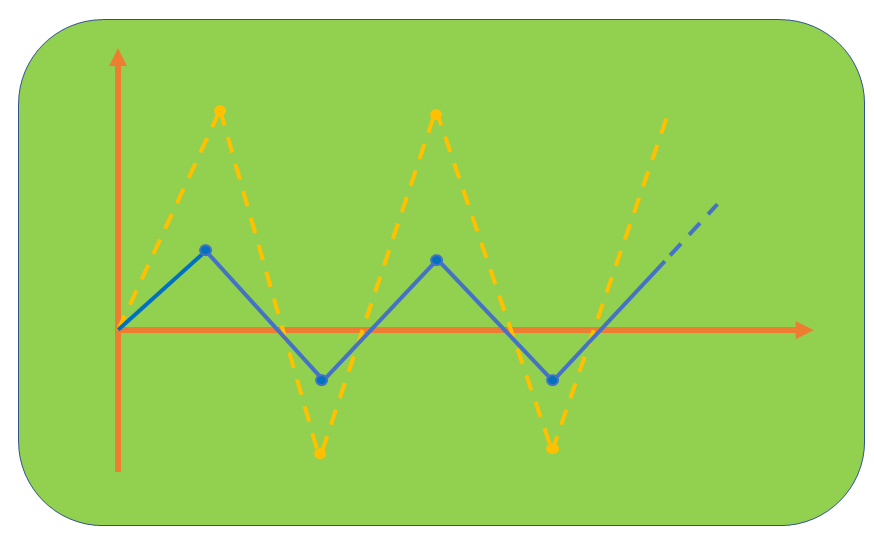
According to the Thermal Shock test diagram below, the white dotted line is the thermal diagram that the test piece must achieve, but in fact the test piece can only be achieved according to the solid blue line diagram. When measuring the test piece does not reach the temperature peak it is subjected to and does not reach the standard thermal shock (thermal shock).
CASE 2:
In this case, the test piece has reached the set temperature (solid blue line) but not within the time required by the standard (dashed white line). Therefore, the tests will have to last much longer than the required time and the rate of change in temperature will be lower than that required by the standard, the test piece will not suffer from thermal shock according to the standard.
That's why it is so important to choose thermal shock test chamber.
ALSO WHEN CHOOSING A THERMAL SHOCK CHAMBER, CUSTOMERS NEED TO UNDERSTAND THE STANDARDS THAT CHAMBERS MEET.
Some common standards for thermal shock are applicable such as MIL-SL-883H,
In particular, product quality complies with the strictest standards set according to US military MIL-ST-883H 1010.8, IEC-60068, IEC-60749, IEC-61747 Technical Committee Standard international electrical engineering, JASO D902 Japanese motor vehicle standards. ISO 9022-2.
Thermal shock test cycle meets the standard
These standards establish unified methods, conditions and procedures for testing electronic equipment, military and aerospace products, automobiles, and motorcycles where reliability is required. set very high.
Select a thermal shock test chamber with the following information:
- Temperature range
- Temperature exchange rate
- Volume (product dimensions and test chamber)
- Sample weight
- Performance of the sample to be tested
- Temperature range

The specifications tables of the thermal shock cabinets define the minimum (min) and maximum (max) temperatures achieved. Almost all climatic chamber manufacturers set the maximum temperature at + 150 ° ~ + 180 ° C, although if required this can be extended to + 200 ° C as a option. Although the maximum temperatures are almost always the same, the minimum temperatures of the chambers using a mechanical cooling system allow them to be divided into two broad categories:
✓ Single cooling system -20 ° ~ -40 ° C
✓ Dual cooling system -50 ° ~ -70 ° C
The dual refrigeration system consists of two refrigeration systems, consisting of two separate compressor units arranged in series so that very low temperatures can be reached.
Sometimes a thermal shock cabinet with a chosen dual refrigeration system does not need to reach an exceptionally low temperature below the desired cooling level, but to have a rapid cooling rate at a low temperature.
- Temperature exchange rate

The rate of increase or decrease in the temperature inside the test chamber is called the temperature exchange rate (expressed in Kelvins or degrees Celsius per minute) and can vary greatly from model to model. , from 6 ° C / min to 10 ° C / min.
The rate of temperature exchange obviously depends on the cooling capacity of the compressor and the heating of the heating rod installed in the chamber. In other words, the stronger the compressor, the faster the cooling rate and the more heat bars are installed in the chamber, the faster the heating rate.
The temperature exchange rates given in the thermal shock test cabinet specifications table generally refer to the equipment performance with the test cabinet being empty (i.e. without a test piece).
- Volume

The main information to consider regarding the product to be tested is: product size, product material, product shape and weight of product under test.
The size of the product allows you to determine the volume of the test cabinet, which is large enough to accommodate comfortably. It is generally best practice that the size of the test piece should not exceed one-third of the volume of the test chamber, although special consideration should be given to the shape of the product under test. In all cases the air shall be able to circulate freely to ensure that the variation and uniformity of temperature are almost equal (within the tolerance specified by the test) over the entire surface. of the test sample.
- Sample weight

The weight of the test piece is also a very important parameter, as large volumes can adversely affect test performance: the performance of the climatic chambers, such as the temperature slope, calculated and specified with empty chamber, i.e. without any mass inside the test chamber. Therefore, when the required value of the required temperature exchange rate for the test piece is close to the value of the temperature exchange rate given in the technical data sheet (with empty chamber), it is necessary to carry out a home inspection. supply room.
Weight is a parameter that must be taken into account for another reason: the test cabinet racks are designed to support specimens up to a certain weight. Therefore, it is best to check the rating plate for what the maximum weight of the test piece is.
If the test piece exceeds the maximum permissible weight, the cabinet accessories include a reinforced bracket or bracket.
- Performance of the sample to be tested
a. The sample works when tested:

When the test piece is connected to a power source (active prototype), it can dissipate heat. In some cases this may be insignificant, while in other cases it should be taken into account, as it may affect chamber performance, as specified above is often indicated with Empty chamber i.e. no volume and no heat dissipation.
Therefore, when the test piece is in operation, the chamber shall remove the heat radiating from the test piece without affecting its performance, in which case the test values are met.
b. Special case

There are also special circumstances in which the test piece may release flammable, explosive, toxic and / or corrosive substances or substances that may generate potentially hazardous gases, depending on the temperature range. they can be attained. In this case, the client is required to consult with HUST VIETNAM to accurately assess the test-related risks.
HUST VIETNAM will help you choose the thermal shock test chambers in the two- or three-zone of VISIONTEC - KOREA are developed based on the testing requirements of customers with maximum aim. performance, efficiency, productivity, reliability and safety.
THANK YOU!
